Camera
Video Lecture


Description
There are several types of Cameras in Threejs. In this video we will experiment with the Perspective and the Orthographic cameras.
The camera properties describe a Frustum which are the dimensions inside the scene that will be rendered.
Perspective Camera
The Perspective projection is designed to mimic the way the human eye sees. It is a very common projection mode used when rendering 3D scenes.
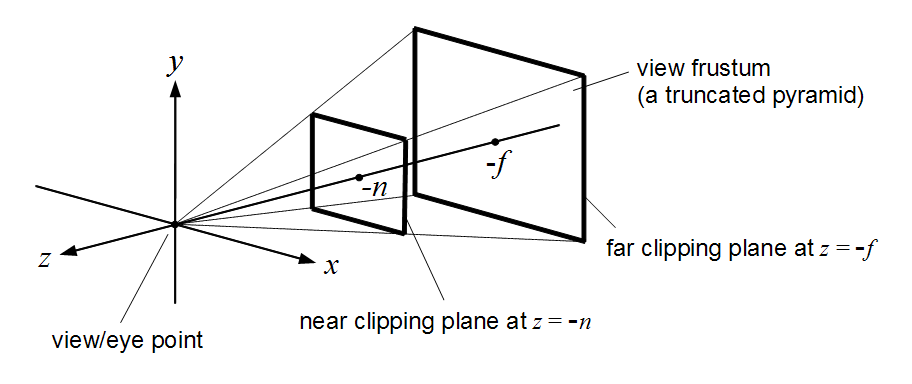
Perspective View Frustum : CC BY-SA 3.0
To begin, replace your ./src/main.ts with the code below.
Lesson Script
./src/main.ts
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63 | import './style.css'
import * as THREE from 'three'
import Stats from 'three/addons/libs/stats.module.js'
import { GUI } from 'dat.gui'
const scene = new THREE.Scene()
scene.add(new THREE.GridHelper())
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000)
//camera.position.set(0, 2, 3)
//camera.lookAt(0, 0.5, 0)
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer()
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement)
window.addEventListener('resize', () => {
camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
})
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry()
const material = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial({ wireframe: true })
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material)
cube.position.y = 0.5
scene.add(cube)
const stats = new Stats()
document.body.appendChild(stats.dom)
const gui = new GUI()
const cameraFolder = gui.addFolder('Camera')
cameraFolder.add(camera.position, 'x', -10, 10)
cameraFolder.add(camera.position, 'y', -10, 10)
cameraFolder.add(camera.position, 'z', -10, 10)
cameraFolder.add(camera, 'fov', 0, 180, 0.01).onChange(() => {
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
})
cameraFolder.add(camera, 'aspect', 0.00001, 10).onChange(() => {
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
})
cameraFolder.add(camera, 'near', 0.01, 10).onChange(() => {
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
})
cameraFolder.add(camera, 'far', 0.01, 10).onChange(() => {
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
})
cameraFolder.open()
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(animate)
//camera.lookAt(0, 0.5, 0)
renderer.render(scene, camera)
stats.update()
}
animate()
|
Working Example
Orthographic Camera
The Orthographic projection is like a cube in itself where the perspective remains constant regardless of its distance from the camera.
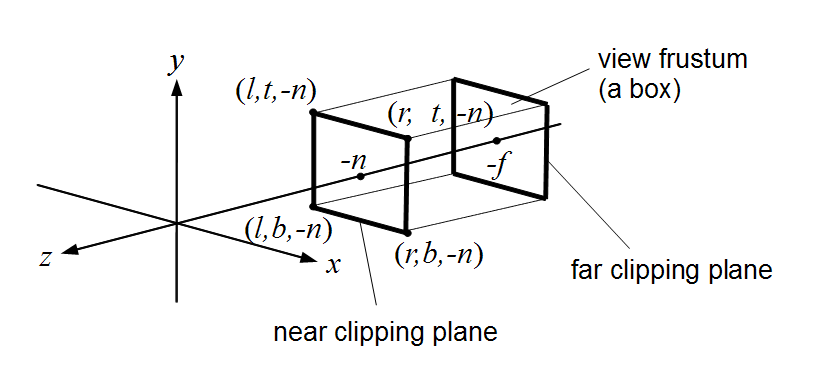
Orthographic View Frustum : CC BY-SA 3.0
./src/main.ts
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69 | import './style.css'
import * as THREE from 'three'
import Stats from 'three/addons/libs/stats.module.js'
import { GUI } from 'dat.gui'
const scene = new THREE.Scene()
scene.add(new THREE.GridHelper())
const camera = new THREE.OrthographicCamera(-4, 4, 4, -4, -5, 10)
camera.position.set(1, 1, 1)
camera.lookAt(0, 0.5, 0)
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer()
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement)
window.addEventListener('resize', () => {
//camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
})
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry()
const material = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial({ wireframe: true })
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material)
cube.position.y = 0.5
scene.add(cube)
const stats = new Stats()
document.body.appendChild(stats.dom)
const gui = new GUI()
const cameraFolder = gui.addFolder('Camera')
// cameraFolder.add(camera.position, 'x', -10, 10)
// cameraFolder.add(camera.position, 'y', -10, 10)
// cameraFolder.add(camera.position, 'z', -10, 10)
cameraFolder.add(camera, 'left', -10, 0).onChange(() => {
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
})
cameraFolder.add(camera, 'right', 0, 10).onChange(() => {
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
})
cameraFolder.add(camera, 'top', 0, 10).onChange(() => {
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
})
cameraFolder.add(camera, 'bottom', -10, 0).onChange(() => {
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
})
cameraFolder.add(camera, 'near', -5, 5).onChange(() => {
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
})
cameraFolder.add(camera, 'far', 0, 10).onChange(() => {
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
})
cameraFolder.open()
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(animate)
//camera.lookAt(0, 0.5, 0)
renderer.render(scene, camera)
stats.update()
}
animate()
|
Working Example
Useful Links
PerspectiveCamera (threejs.org)
OrthographicCamera (threejs.org)
Camera (threejs.org)
Viewing Frustum (wikipedia)
Different Projection Models (wikipedia)
Perspective Projection (wikipedia)